2 simple geometrical elements are responsible to describe any geometrical shape. These are the Straight Line and the Circle. If you connect a line with at least one external non-collinear point you get a plane. If you extrapolate a circle towards an external point in perpendicular direction to the center point you get a cylinder.... Continue Reading →
MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING – Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing_What is the CIRCULARITY tolerance?
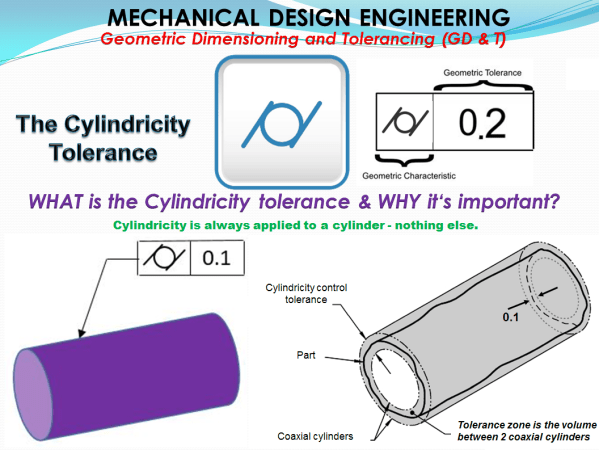
In mechanical design of things, any object is defined by 2 geometrical forms: the straight line and the circle. A combination between the 2, results in complex surfaces. Therefore we can clearly say that next to the straight line, the circle is the second basic geometrical form in the entire technique. Maintaining the circularity (roundness)... Continue Reading →
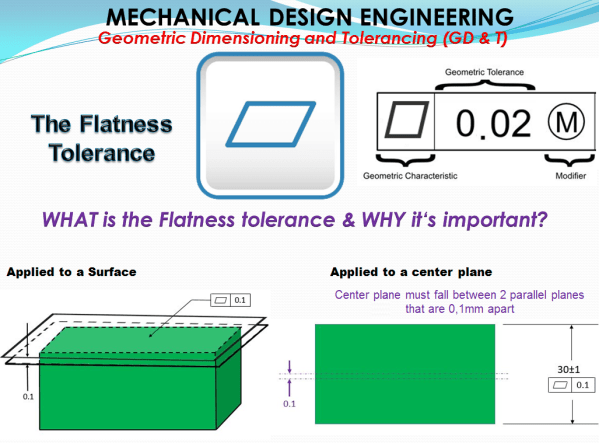
MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING – Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing_What is the FLATNESS tolerance?
All the time when you want to make sure something is accurately closed/sealed the parts that are joined in your mechanical assembly product must have a specified restriction for how tight that closure must be. For this reason is essential that these parts are designed by default with such important specification which in Mechanical Design... Continue Reading →
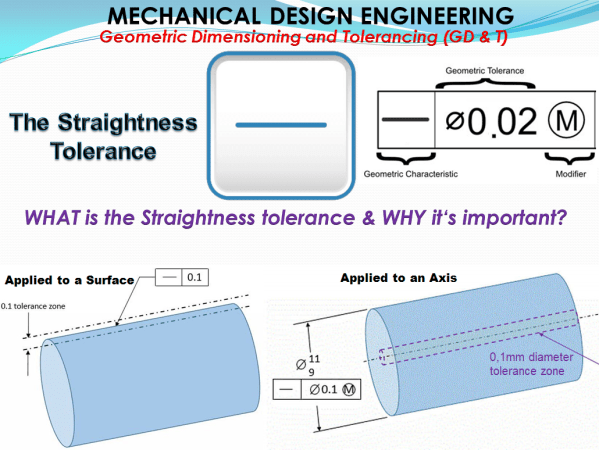
MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING – Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing_What is the STRAIGHTNESS tolerance?
In every new product development process there are different stages to go through until the first official release is available for mass production. In early stages of product development you have the opportunity to test as many prototypes as possible, nothing must be strictly defined; however after few iterations, many tests and approval processes you... Continue Reading →
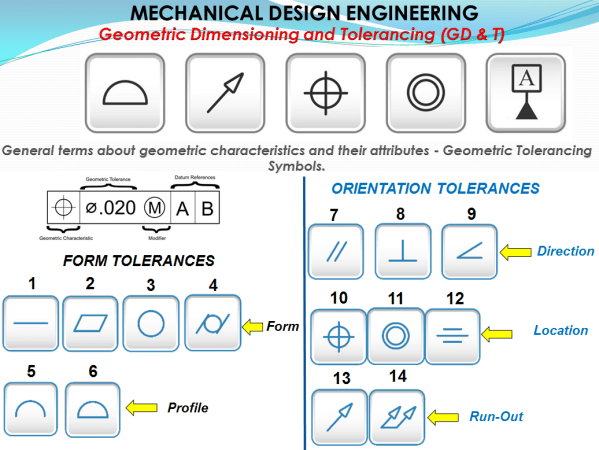
MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING – GD + T – General terms about geometric characteristics and their attributes.
Geometric Dimensioning And Tolerancing defines a functionality of a part and because the part drawing is the first tool people use in order to manufacture a part, the designer must clearly specify all the necessary characteristics which will communicate further how that part must be produced and how it will finally work. The part drawing... Continue Reading →
MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING – When do we use GD + T and How does it work?
The term "Product Design" covers a large area of possibilities for different applications. We have Product Design in Mechanical Engineering but this is also done in Software Engineering (i.e App development, WebSites, AI applications, etc), Electrical Engineering (i.e. PCB design, Semiconductors, Superconductors,), Nanotechnology, etc, all these have their own Product Design guidelines and norms. But... Continue Reading →
MECHANICAL DESIGN ENGINEERING – Why you MUST apply Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing on your Product Design?
In product development environment there is nowadays a commonly and often mentioned acronym as CAD which stands for: Computer Aided Design. That is to say that the convetional way how mechanical engineering was done in the past can now be done with assisted by a computer programm. And that is excelent. It clearly speeds up... Continue Reading →